China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News: This headline sparks a fascinating exploration of China’s manufacturing dominance. We’ll delve into its historical rise, examining key factors like its vast workforce, government support, and efficient supply chains. We’ll also confront the challenges – rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and geopolitical tensions – and consider the future of Chinese manufacturing in a rapidly changing global landscape.
So, the Hacker News thread on China’s manufacturing dominance is fascinating, right? It makes you think about the global economy and how things get made. It’s a stark contrast to the personal struggles of someone like Jermaine Burton, whose situation, as detailed in this article, Jermaine Burton left home by Bengals, gets eviction notice , highlights the human element often overlooked in discussions of large-scale manufacturing.
Ultimately, both stories underscore the complexities of modern life and global interconnectedness.
From its humble beginnings to its current position as a global manufacturing giant, China’s journey is a compelling case study in economic development. This analysis will dissect its strengths and weaknesses, offering a balanced perspective on its continued influence on global supply chains and the broader economic order. We’ll look at the impact of automation, technological advancements, and potential shifts in the global manufacturing landscape.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing superpower is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy, China has become the global factory, producing a vast array of goods for both domestic and international markets. This dominance wasn’t achieved overnight; it’s the result of decades of strategic planning, investment, and adaptation.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – the sheer scale of production is mind-boggling! It makes you appreciate the precision needed in fields like surgical technology, which is why finding a good program is key. If you’re interested in becoming a surgical tech, check out this site for accredited surgical tech programs near me with clinical rotations to learn more.
Then, consider how many of the tools used in those programs are likely manufactured in China – it really connects the global economy in unexpected ways!
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Perspective
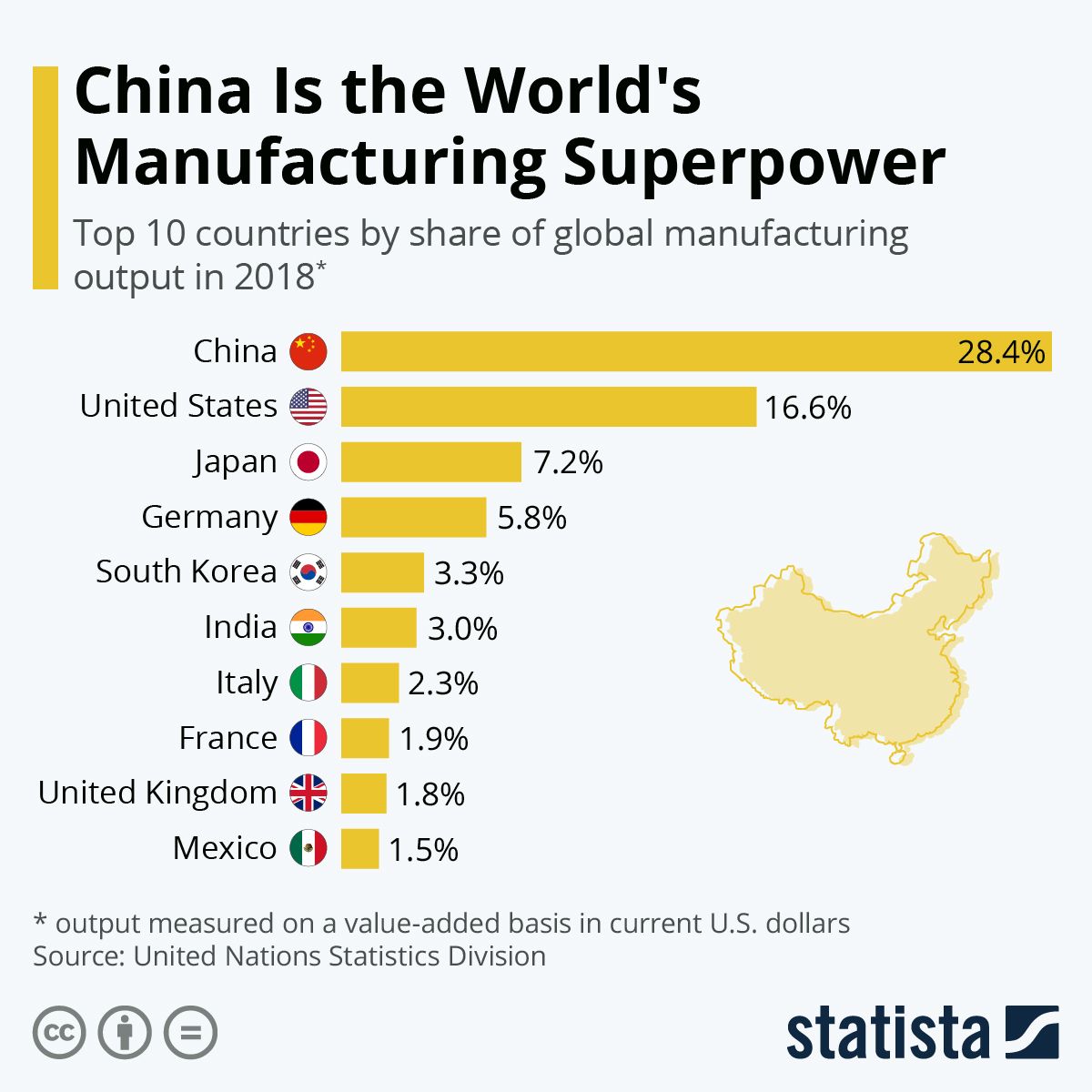
China’s manufacturing sector’s evolution is a multifaceted journey marked by significant milestones and transformative shifts. Key factors, including government policies, infrastructure development, and a vast, adaptable workforce, propelled its growth. Comparing China’s trajectory with other major economies reveals its exceptional speed and scale.
| Date | Event | Impact | Supporting Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1978 | Economic Reforms initiated by Deng Xiaoping | Opened the door for foreign investment and market-oriented reforms, laying the foundation for manufacturing growth. | GDP growth surged from an average of 5% in the 1970s to over 9% annually in the 1980s and 1990s. |
| 1980s-1990s | Establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) | Attracted foreign investment and fostered export-oriented manufacturing. | SEZs accounted for a significant portion of China’s export growth during this period. |
| 2001 | China’s accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Further integrated China into the global economy, significantly boosting trade and investment. | China’s share of global exports increased dramatically after WTO accession. |
| 2010s-Present | Focus on technological advancement and domestic consumption | Shift towards higher value-added manufacturing and reduced reliance on low-cost labor. | Increased investment in R&D and automation. |
Strengths of China’s Manufacturing Ecosystem, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
Several interconnected factors contribute to China’s manufacturing prowess. A massive and adaptable workforce, supportive government policies, efficient supply chains, and cost-effectiveness are all crucial components of its success.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those components end up in EVs, right? Check out how well Rivian’s doing today; Rivian stock has its best day ever after EV maker reports 2024 , which highlights the growing EV market. This all underscores how crucial China’s role is in the global supply chain, even for American companies.
- Vast and Skilled Labor Force: China boasts a large and relatively low-cost labor pool, although this is changing with rising wages.
- Government Policies and Infrastructure: Government investment in infrastructure (ports, roads, energy) and supportive policies (tax incentives, subsidies) has been instrumental.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: Highly developed and efficient supply chains, coupled with extensive logistics networks, ensure smooth and cost-effective production and distribution.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Countries:
- Lower labor costs (historically, though this is changing).
- Access to raw materials and components.
- Government subsidies and tax incentives.
- Economies of scale due to large production volumes.
Challenges and Weaknesses in China’s Manufacturing Sector

Despite its dominance, China’s manufacturing sector faces several challenges. Over-reliance on China for manufacturing poses risks, and rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and geopolitical tensions are all significant factors.
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Strategies | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Over-reliance on China for manufacturing | Supply chain disruptions, geopolitical vulnerability | Diversification of manufacturing locations, development of domestic supply chains in other countries | Reduced dependence on China, increased resilience to disruptions |
| Rising labor costs and automation | Increased production costs, potential job displacement | Investment in automation and robotics, upskilling the workforce | Improved efficiency, higher value-added manufacturing |
| Environmental regulations and sustainability concerns | Increased production costs, pressure to adopt sustainable practices | Investment in cleaner technologies, stricter enforcement of environmental regulations | Reduced pollution, improved environmental sustainability |
| Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes | Trade barriers, uncertainty for businesses | Strengthening international cooperation, diversification of trade partners | Reduced reliance on specific markets, improved trade relations |
The Future of Manufacturing in China
Predicting the future of Chinese manufacturing requires considering several interconnected trends. Maintaining dominance will depend on adapting to technological advancements, navigating geopolitical challenges, and fostering innovation.
One potential scenario involves a gradual shift towards higher-value manufacturing, driven by technological advancements and a focus on domestic consumption. China could become a hub for advanced manufacturing and technological innovation, while other countries focus on niche markets or specific aspects of the supply chain. This would require substantial investment in research and development, workforce upskilling, and the adoption of sustainable practices.
Impact on Global Supply Chains

China’s manufacturing capabilities significantly influence global supply chains, creating both opportunities and vulnerabilities. The interconnectedness of global manufacturing means disruptions in China can have ripple effects across numerous industries.
Industries Heavily Reliant on Chinese Manufacturing: Electronics, textiles, apparel, toys, and many consumer goods sectors are heavily reliant on China.
Potential Disruptions Caused by Shifts in Chinese Manufacturing:
- Increased production costs.
- Supply chain disruptions.
- Geopolitical risks.
- Changes in product quality or availability.
Technological Advancements and Automation
Automation and robotics are rapidly transforming the Chinese manufacturing landscape. China’s adoption rate of advanced technologies is increasing, although it still lags behind some developed economies in certain areas. This integration is reshaping the nature of work and driving efficiency gains.
A typical Chinese factory integrating AI and automation might feature robotic arms performing repetitive tasks on assembly lines, AI-powered quality control systems analyzing products in real-time, and predictive maintenance algorithms optimizing equipment performance. Data analytics would be used to monitor production efficiency and optimize resource allocation. While human workers remain essential, their roles are evolving towards more skilled and supervisory functions.
End of Discussion
China’s manufacturing superpower status is undeniable, but its future isn’t guaranteed. While its strengths remain significant, challenges related to rising costs, environmental concerns, and geopolitical factors require careful consideration. The coming decade will be crucial, as China navigates technological advancements and evolving global dynamics to maintain its position. Understanding this complex interplay is essential for anyone involved in global trade and manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the biggest risks of relying too heavily on Chinese manufacturing?
Over-reliance creates vulnerabilities to supply chain disruptions, geopolitical instability, and potential trade wars. Diversifying manufacturing sources is key to mitigating these risks.
How is China addressing environmental concerns in its manufacturing sector?
China is implementing stricter environmental regulations and investing in greener technologies, though challenges remain in balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
What role does automation play in China’s manufacturing future?
Automation is crucial for China to maintain competitiveness by increasing efficiency and addressing rising labor costs. This involves significant investment in robotics and AI.
